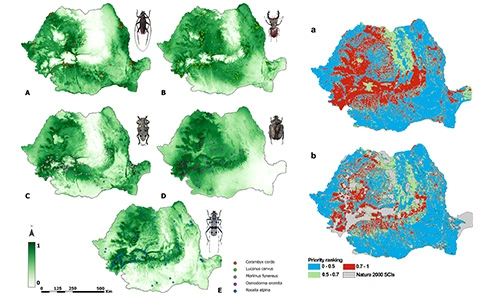
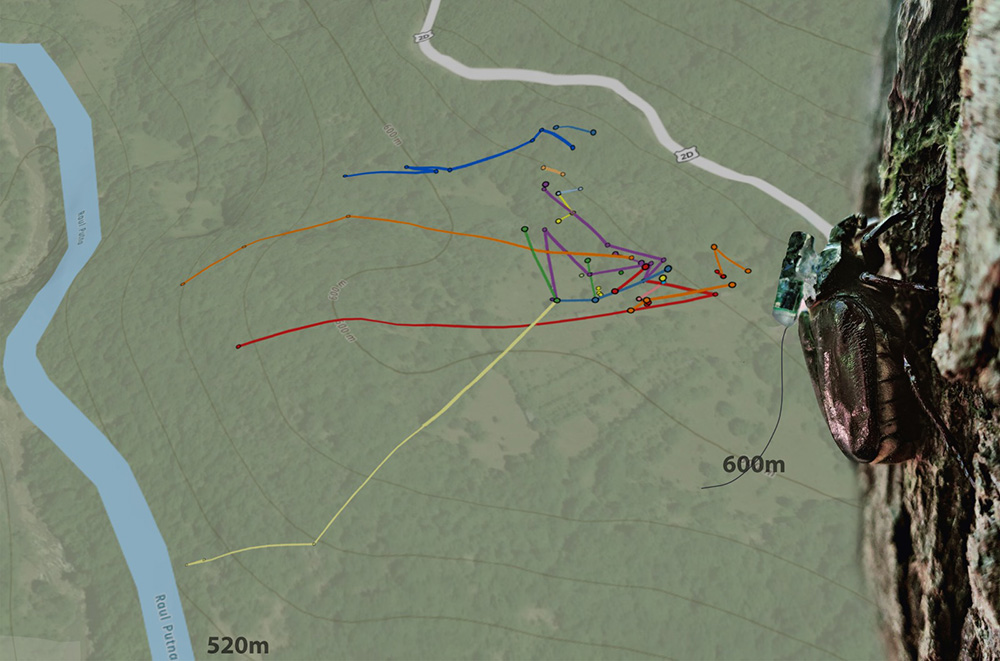
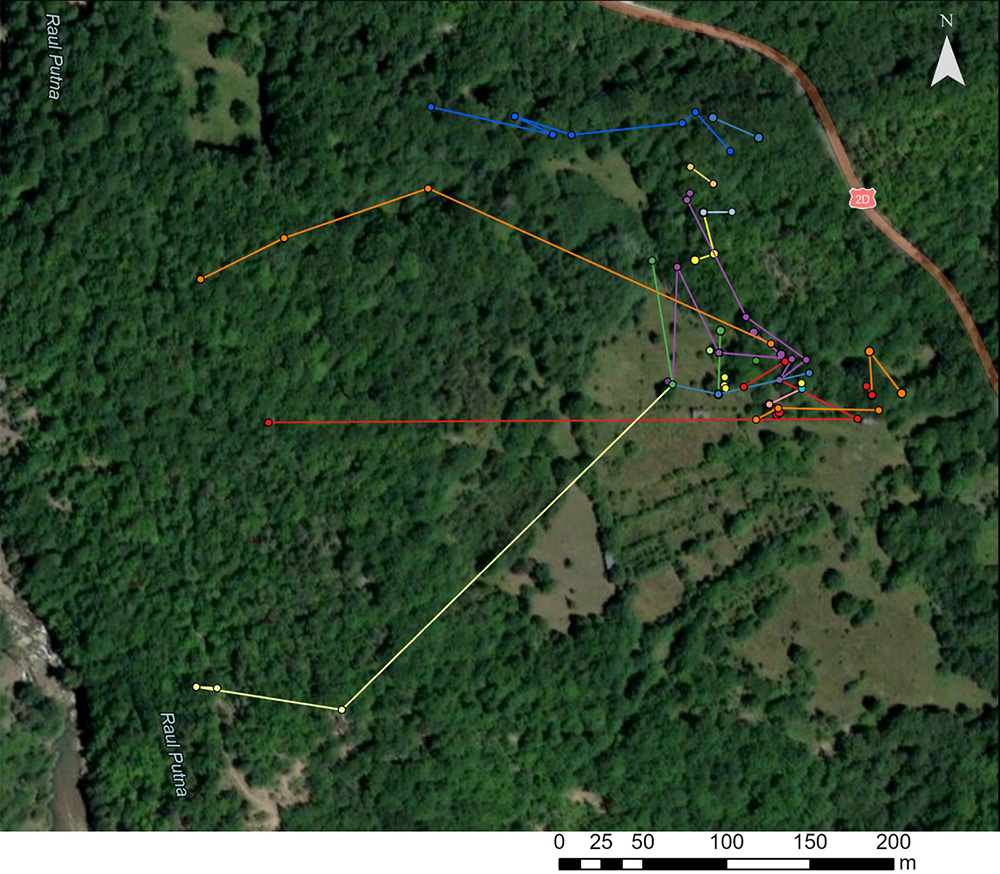
Telemetry study for Osmoderma hermita
To document the movement and habitat selection of the priority species Osmoderma eremita, the LIFE Rosalia team installed 20 VHF transmitters on individuals belonging to this species. To avoid affecting the behavior and movement of the species, transmitters were only attached to individuals weighing over 1.5g (the transmitter represents at most 10% of the individual’s weight).
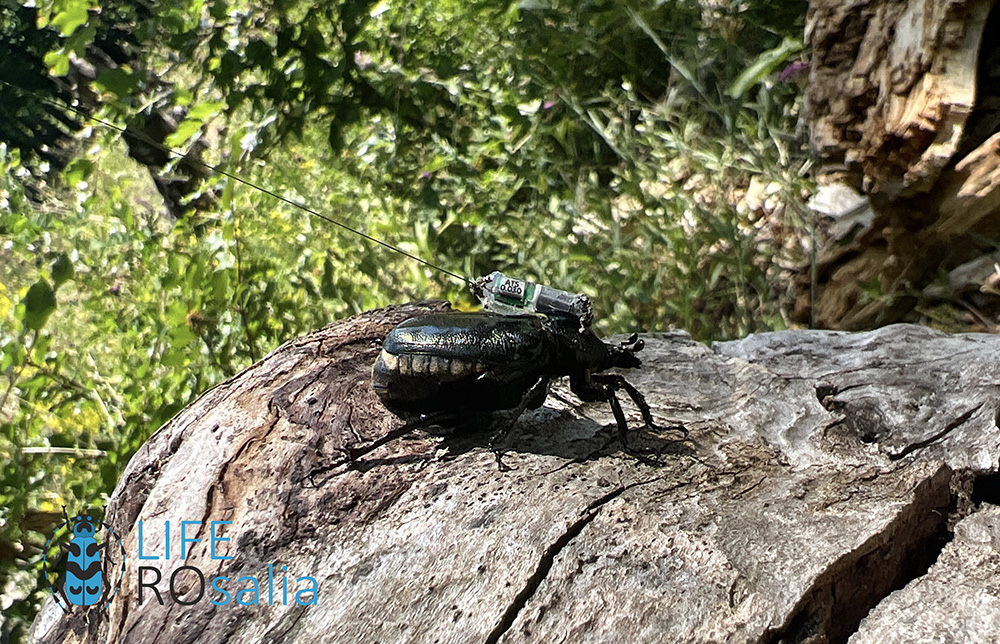

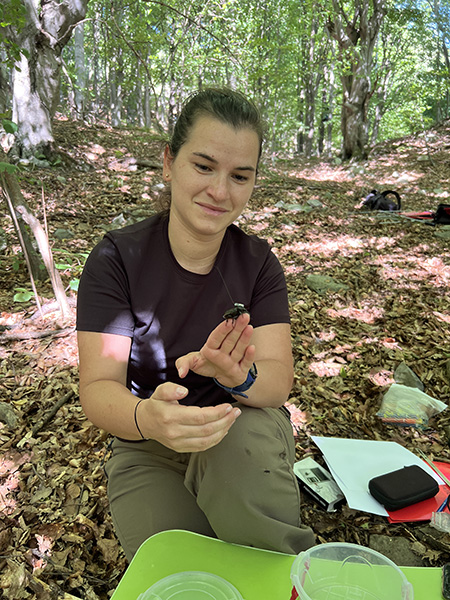
The insects were captured using non-lethal flight interception traps and were checked every 3 hours between 10:00-18:00. The captured insects were measured to see if they could be fitted with transmitters, and then they were released in the vicinity of the capture site. The coordinates of each individual with a transmitter attached were recorded at each trap monitoring.

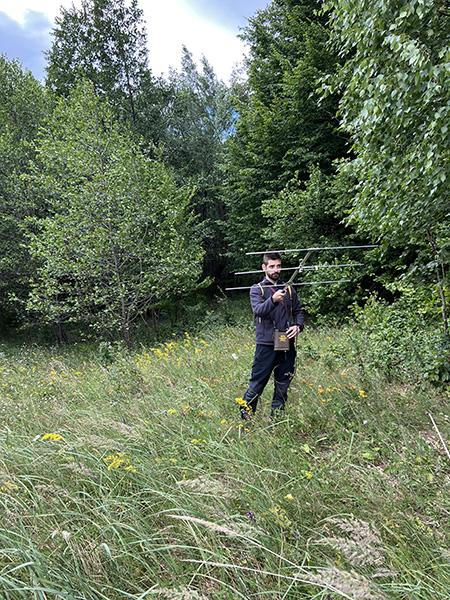
During the movement ecology monitoring for the priority species Osmoderma eremita, individuals equipped VHF transmitters were observed to travel distances ranging from 6m to 400m (measured in a straight line). Individuals who did not change their position either moved vertically within the same tree or were stationary in tree cavities.

In addition, observations were made on the forest and habitat in the monitoring area to determine the forest structure in the 50-meter buffer zone of all species locations. Information was recorded for each tree regarding its morphology and structure: species, diameter, height, location, condition, canopy, and tree characteristics (cracks, water-filled holes, cavities with decay, bark loss, and insect galleries).
Why is monitoring the movement of wildlife important?
Monitoring the movement of saproxylic insects is important for several reasons:
- Indicators of ecosystem health: Saproxylic insects are sensitive to environmental changes such as pollution, deforestation, and climate change. Therefore, monitoring them can provide valuable information about the health of ecosystems.
- Assessment of human activities impact: Saproxylic insects are often affected by human activities such as deforestation and urbanization. Monitoring them can help assess the impact of these activities on ecosystems and identify measures to protect and conserve saproxylic insects and their habitats.
- Protection of biodiversity: Saproxylic insects play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. Monitoring them can help identify changes in their behavior and geographic distribution, as well as detect problems that may arise from anthropogenic pressure on species habitats.
In general, monitoring the movement of wildlife is important to better understand the interaction between wildlife, their environment, and human activities.